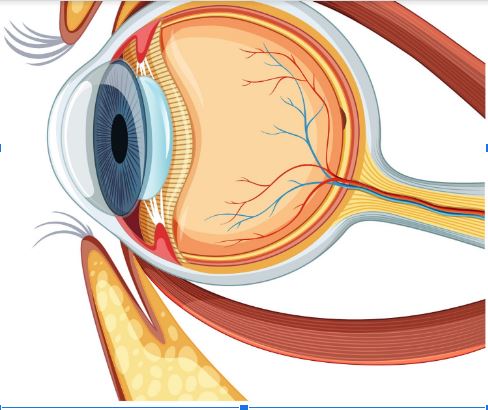
The retina is a group of sensitive cells located in the back of the eye in which there are light receptors that interact with it, then receive visual information and send signals to the brain in order for the vision process to occur. Some of the problems that occur in the retina can result in permanent vision loss.
Retinal detachment is one of the problems that can affect the retina which occurs when the retina separates from the basic layer of supportive tissue in the back of the eye, and this separation can be in a small part of the retina. In this case, immediate treatment must be done so as not to occur any complications which could lead to vision loss.
Many sudden changes occur through which a person can infer the detachment of the retina, such as eye floaters & dark side vision, and therefore if you feel any of these symptoms, the Royal Spanish Center advises you to get quick and immediate treatment as soon as possible.
Types of retinal detachment
Retinal detachment caused by retinitis:
This type is the most common among the types of retinal detachment, there is a hole or tear in the retina and this leads to the leakage of fluid from inside the eye to the retina, which results in the separation of the membrane responsible for providing the retina with the nutrition and oxygen it needs.
Surgical retinal detachment:
This type is less common than the previous type. This type of retinal detachment occurs when scar tissue, which is a thin layer on top of the retina, contracts and pulls on the retina, causing vision problems like blurring and foggy vision.
Exudative detachment:
This separation occurs as a result of some diseases such as cancer behind the retina, the accumulation of fluid behind the retina, which leads to inflammation, and the abnormal growth of some blood vessels, which leads to the accumulation of proteins that leak behind the retina.
Symptoms of retinal detachment

Retinal detachment patient feels some symptoms, which are signs of a problem that requires immediate treatment, and the most important of these symptoms are:
- Sudden and quick flashes of light in the vision.
- A significant increase in spots, lines and dots that appear excessively in a person’s field of vision and are known as eye floaters.
- Blurry vision as if the patient sees a transparent curtain in front of his field of vision.
- Feeling of heaviness in the eyes.
- Seeing shadows begin to move from the peripheral vision to the center of vision.
- See straight lines as curves.
Risk Factors of Retinal Detachment
- History: as a family with a retinal detachment can pass the disease on to their family members genetically.
- Serious eye injury or trauma.
- Some eye surgeries such as cataract surgery
- Certain chronic diseases, such as diabetes, may make a person more likely to develop retinal detachment.
- Certain eye diseases such as iritis, severe myopia, or thinning of the surrounding retina.
Diagnosis
Ultrasound is also used in some cases, but if bleeding occurs in the eye, it will be difficult to see the retina.
Tips to avoid retinal detachment
- A person should undergo a regular eye examination, especially if he has myopia, because severe myopia is one of the factors that make a person more susceptible to retinal detachment, and therefore it is necessary for a person to go for a vision examination every 3 or 6 months to make sure that there is no Indications of retinal detachment. Regular eye exams can reveal any thinning or tearing that indicates retinal detachment.
- Be sure to wear sunglasses to avoid UV damage
- Be sure to wear protective eyewear if you play some types of sports, especially extreme sports such as wrestling.
Treatment
The appropriate type of treatment
- Determined based on the degree and type of retinal detachment.
- so your doctor may recommend laser surgery, cryotherapy, or other types of surgery.
- to repair any retinal tears or fractures and reconnect the retina.
- Sometimes the ophthalmologist may use more than one of these treatments at the same time.
surgery
- Laser surgery or cryotherapy is done after the patient is given a local anesthetic to numb the eye,.
- and through the use of a freezing probe or medical laser.
- any tears or cracks in the retina are closed, and after the procedure it is recommended.
- to avoid violent activities that may shake the eyes.
- such as running – for a few weeks or as advised by the doctor who performed the procedure.
There is another type of surgery. which is used if a retinal detachment develops. and if the doctor finds that a large part of the retina has detached.
Recovery after surgery
After the retinal detachment surgery, the doctor recommends:
- using drops to prevent any infection that may affect the eye.
- and the patient may recommend wearing a patch for a day.
- or more after the surgery.
- in order to preserve it and get the best possible result.
The patient needs a period ranging from two weeks and up to 4 weeks to recover after the surgery, and the more the patient adheres to the doctor’s instructions, the more this contributes to accelerating the recovery period.
Post-surgery tips
- The patient must take a sufficient amount of rest whenever he needs it.
- so that he does not suffer from eye strain.
- Avoid lifting any heavy objects or moving the head violently and suddenly.
- Take a break from work for a period of up to two weeks.
- especially if it requires intense eye focus or the person uses the computer for long periods.
- Adhere to all medications and eye drops prescribed by the doctor.
- If you feel any swelling in the eye, a cold bag or ice can be placed for 10 to 20 minutes.
- until you feel an improvement in the pain, and it is preferable to consult a doctor before any home remedy.
- The face is washed with water only, and violence in the eye area is avoided.