Strabismus is a common condition among children. About 4% of all children have strabismus.
Definition:
a visual defect in which the eyes are misaligned and point in different directions. One eye may look straight ahead, while the other eye turns inward, outward, upward or downward. You may always notice the misalignment, or it may come and go.
Underlying causes of strabismus
The exact cause of strabismus is not fully understood. Yet Strabismus is common among children with disorders that affect the brain, such as: Cerebral palsy, Down syndrome, Hydrocephalus, and Brain tumors as the brain controls the eye muscles movement.For further explanation it is about Six eye muscles, controlling eye movement, are attached to the outside of each eye. In each eye, two muscles move the eye right or left. The other four muscles move it up or down and at an angle. So in order To line up and focus both eyes on a single target, all of the muscles in each eye must be coordinated and move together which is controlled mainly by the brain.
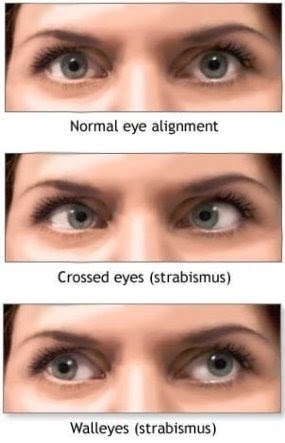
Strabismus diagnosis and check up
Royal Spanish center always gives its sincere advice that all children have their vision checked by their pediatrician, family doctor or ophthalmologist (medical eye doctor) at or before 4th birthday. If there is a family history of strabismus or Amblyopia, an ophthalmologist should check vision even earlier than age of three. The eyes of infants often seem to be crossed. Young children often have a wide, flat nose and a fold of skin at the inner eyelid that can make the eyes appear crossed. This appearance of strabismus may improve as the child grows.
What is False strabismus?
Sometimes a child will not outgrow true strabismus. An ophthalmologist can usually tell the difference between true and false strabismus.
Common Types of Strabismus and Treatment :
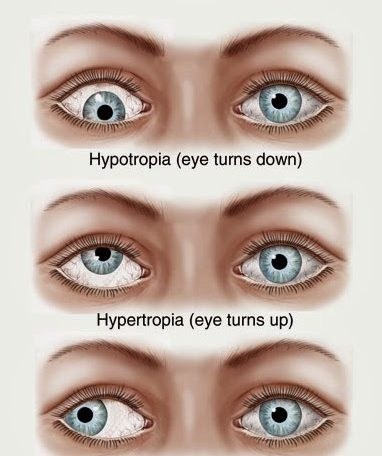
Esotropia
Definition: where the eye turns inward, is the most common type of strabismus in infants. Young children with esotropia do not use their eyes together.
Treatment: early surgery can align the eyes. During surgery for esotropia, the tension of the eye muscles in one or both eyes is adjusted.
Accommodative esotropia
Definition:
a common form of esotropia that occurs in farsighted children two years or older.When a child is young, he or she can focus the eyes to adjust for the farsightedness, but the focusing effort (accommodation) to see clearly causes the eyes to cross.
Treatment:
- Glasses : reduce the focusing effort and can straighten the eyes.
- Bifocals are needed for close work.
- Eye drops, ointments can be used to straighten the eyes.
- Special lenses called prisms can be used to straighten the eyes.
Exotropia
Definition
an outward turning eye, is another common type of strabismus. This occurs most often when a child is focusing on distant objects. The exotropia may occur only from time to time, particularly when a child is daydreaming, ill or tired.Parents notice that the child squints one eye in bright sunlight.
Treatment:
- Glasses: reduce the focusing effort and can straighten the eyes.
- Exercises: Covering or patching the strong eye to improve Amblyopia is often necessary
- Prisms may reduce or help control the outward turning eye
- Surgery is often needed.
What is Strabismus surgery?
The ophthalmologist start to make a small incision in the tissue covering the eye to reach the eye muscles and there is no removal from the socket during any step of the surgery . Certain muscles are repositioned during the surgery, depending on which direction the eye is turning.
It may be necessary to perform surgery on one or both eyes depending on the case of courseWhen strabismus surgery is performed on children, a general anesthetic is a must while Local anesthesia is an option for adults.
Advantages of Strabismus surgery
- null
- Safe treatment for eye misalignment
- Very Effective
- Rapid Recovery time.
- People are usually able to resume their normal activities within a few days.
- early surgery offers the best chance for the eyes to work well together
- easier for children to undergo such surgery before school age
Our Services :
Spanish Center for Eyes, LASIK and Cosmetics offers comprehensive eye-care packages for international patients, and our dedicated professionals will take care of all aspects- right from helping to plan the package to ensure their treatment period is comfortable and hassle – free.
Related Services:

